

Passage through complex strictures is usually difficult. ( 1) Complex strictures are longer, crooked, more narrow, and have a diameter less than 12 mm.
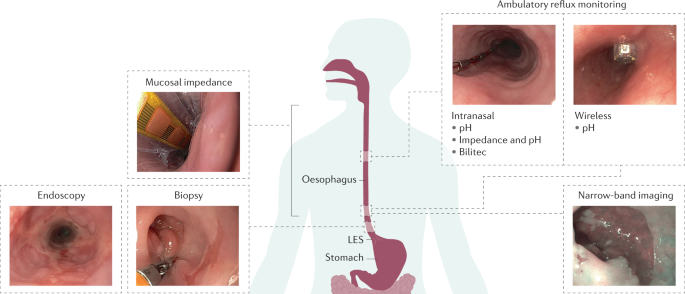
( 9) Endoscopes can easily pass through simple strictures for examination and treatment. Simple strictures are short, straight, symmetrical and have a diameter greater than 12mm. Peptic strictures can be separated into two categories: simple and complex. ( 9) A normal esophagus is about 30 mm in diameter. ( 9) ( 11) Patients typically complain of difficulty swallowing when the stricture narrows the esophagus to less than 12mm in diameter. Though peptic strictures are usually only 1-4cm long and are typically benign, bigger strictures can cause difficulty swallowing solid foods. ( 10) ( 11) Heavy users of alcohol are also known to have a higher risk of peptic strictures. ( 9) The condition is typically found in older people with a long history of ERD. ( 8) ( 9) Peptic strictures can narrow the diameter of the esophagus by up to 13mm. A peptic stricture is a narrowing of the lower esophagus caused by a thickening and scarring of tissue due to long-term ERD and acid damage. ( 2) Most NERD patients remain stable long-term. ( 2)Ĭhronic esophagitis can lead to complications like peptic strictures. ( 2) A study of NERD patients reported 24.9% progressing to grade A/B ERD and only. ( 3)Ī progression from NERD to severe ERD however, is possible and well known but this represents a minority of patients. ( 2) ( 3) A study showed that NERD patients taken off of reflux medication do not progress to ERD but relapse back to NERD symptoms. For decades NERD was seen as a disease that progressed to ERD, if left untreated, but recent research has indicated that NERD and ERD may be two distinct diseases. Non-erosive esophagitis is somewhat of a mystery to the medical community and its pathology is not fully understood. ( 1) ( 6) Non-erosive esophagitis (NERD) patients show no signs of injury to the esophagus in endoscopic examinations but still suffer refractory GERD/LPR symptoms and an impairment on quality of life similar to ERD patients. Most GERD patients have non-erosive esophagitis. ( 5) Only about 30% of GERD/LPR patients have erosive esophagitis. ( 6) A study showed that patients with esophagitis experienced nocturnal acid reflux which can lead to peptic strictures or Barrett’s esophagus. ( 4) Severe erosions involving the circumference of the esophagus are Grade D. Erosions that connect between two or more mucosal folds are grade C. Small single erosions that are classified smaller than 5cm are identified as grade A.( 1) Erosions that are more than 5cm long are grade B. Mucosal breaks are identified with a scale of A-D which is called the Los Angeles criteria. ( 2) Erosive esophagitis is more serious and is characterized by red sores, lesions, and ulcerations on the esophagus, known as mucosal breaks. Medical literature has identified two kinds of esophagitis, erosive (ERD) and nonerosive (NERD).

Esophagitis refers to the inflammation of the esophagus caused by prolonged esophageal acid exposure. Constant, long-term acid reflux disease can lead to complications like peptic strictures, Barrett’s Esophagus, and esophageal cancer.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
